
In Word, you can delete a page in the middle or at the end of a document using several strategies. You can delete blank pages or pages that contain text and other content. Blank pages can be caused by unnecessary hard returns (pressing Enter too many times), manual page breaks, section breaks, paragraph formatting and tables so you will need to determine what is causing a blank page to remove it.
Note: Buttons and Ribbon tabs may display in a different way (with or without text) depending on your version of Word, the size of your screen and your Control Panel settings. For newer versions of Word, Ribbon tabs may appear with different names.
Do you want to learn more about Microsoft Word? Check out our virtual classroom or in-person classroom Word courses >
In this article, we'll review 7 ways to delete a page in Word (quick links):
To delete a page with content in a Word document:
If extra or blank pages appear in the middle or end of a document, they may be caused by unnecessary hard returns (which are created each time you press Enter).
To delete a page by deleting hard returns:
In the following example, extra hard returns have been inserted in a document:

If a manual page break has been inserted in a document, this may also cause extra or blank pages.
To delete a page by deleting a manual page break:
In the following example, a manual page break has been inserted in a document:

You can't delete manual page breaks or section breaks if Track Changes is turned on.
To turn off Track Changes:
Track Changes appears in the Tracking group on the Review tab in the Ribbon:
You can also press Ctrl + Shift + E to turn off Track Changes.
If you are having difficulty selecting and deleting a section or page break, you can go to Draft View to select and delete it:
Draft and Print Layout appear in the Views group on the View tab in the Ribbon:
Unnecessary section breaks may also cause extra or blank pages.
To delete a page by deleting a section break:
It is important to note that sections contain specific formatting for the section. If you delete a section break, margins, page orientation and headers and footers may change.
In the following example, a section break has been inserted in a document:

If you have difficulty deleting a manual section break, turn off Track Changes (as noted in deleting a manual page break).
Extra pages can also be caused by paragraph formatting.
If an extra or blank page is occurring and you do not see extra hard returns, a manual page break or a section break (with Show/Hide ¶ on), you may need to change paragraph formatting.
To change paragraph formatting to delete an unwanted page:
The Paragraph dialog box appears as follows with the Line and Page Breaks tab selected:
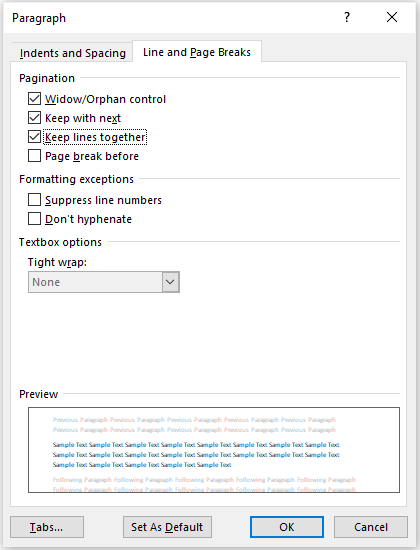
Paragraph formatting options may have been included in a style (such as Heading 1 or Heading 2). If that is the case, you will need to edit the style and change the pagination options in the style.
You can delete a page using the Navigation Pane as well (although this method may not have the desired result depending on the cause of the extra or blank page).
To delete a page using the Navigation Pane:
The Navigation Pane displays thumbnails of the pages in the document when the Pages tab is selected:
 Navigation Pane in Word." width="331" height="651" />
Navigation Pane in Word." width="331" height="651" />
To display the Navigation Pane using a keyboard shortcut, press Ctrl + F. This will display the Navigation Pane with the Results tab selected. Click the Pages tab to display pages.
If you insert a table in a document, Word will always insert a paragraph after the table. You can't delete the paragraph following a table and this may cause a blank page if the table is at the end of the document. You can select the blank paragraph after the table and change the font size to a smaller size as a workaround.
Since there are many reasons extra or blank pages are created in Word, you may need to try different strategies to delete a page.
Did you find this article helpful? If you would like to receive new articles, JOIN our email list.